Fight, Flight, or Freeze — Releasing Organizational Trauma
A presentation at DevOpsDays Tel Aviv 2019 in in Tel Aviv-Yafo, Israel by Matt Stratton
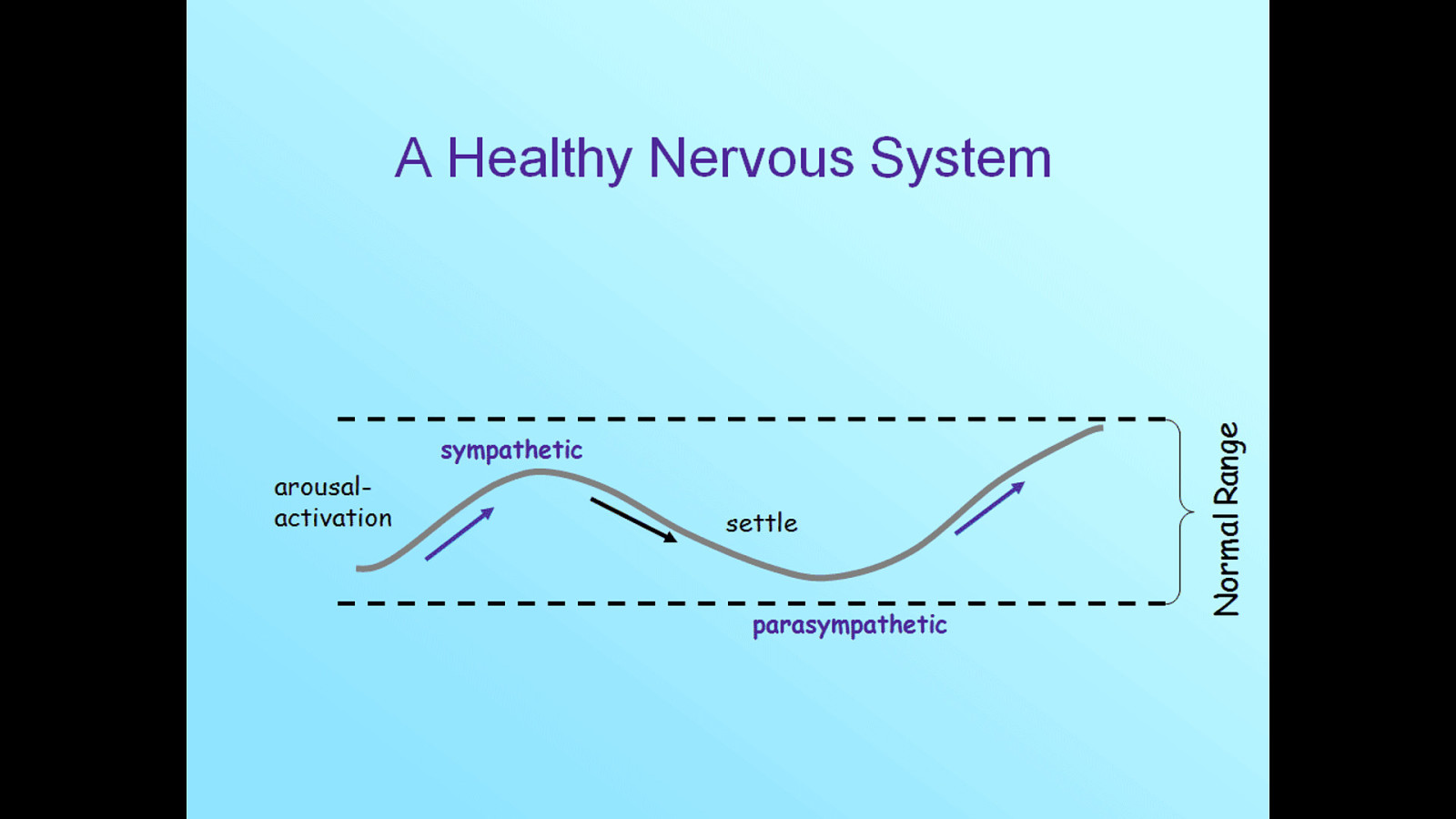
When humans are faced with a traumatic experience, our brains kick in with survival mechanisms. These mechanisms are the familiar fight or flight response, but can also include the freeze response - which occurs when we are terrified or feel that there is no chance of escape.
In this talk I will explain the background of fight, flight, and freeze, and how it applies to organizations. Based on my own experiences with post-traumatic stress (PTS), I will give examples and suggestions on how to identify your own organizational trauma and how to help heal it.
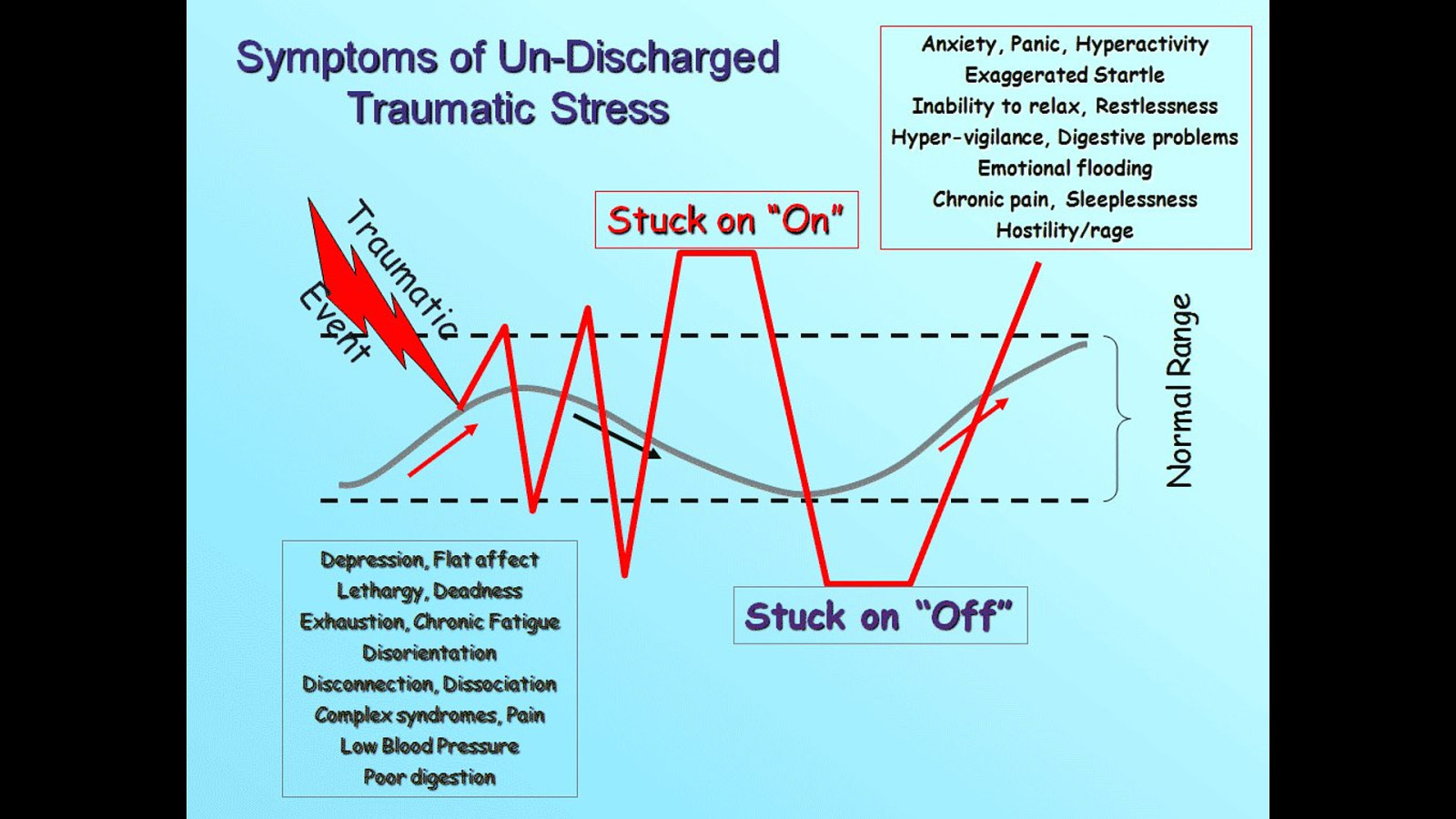
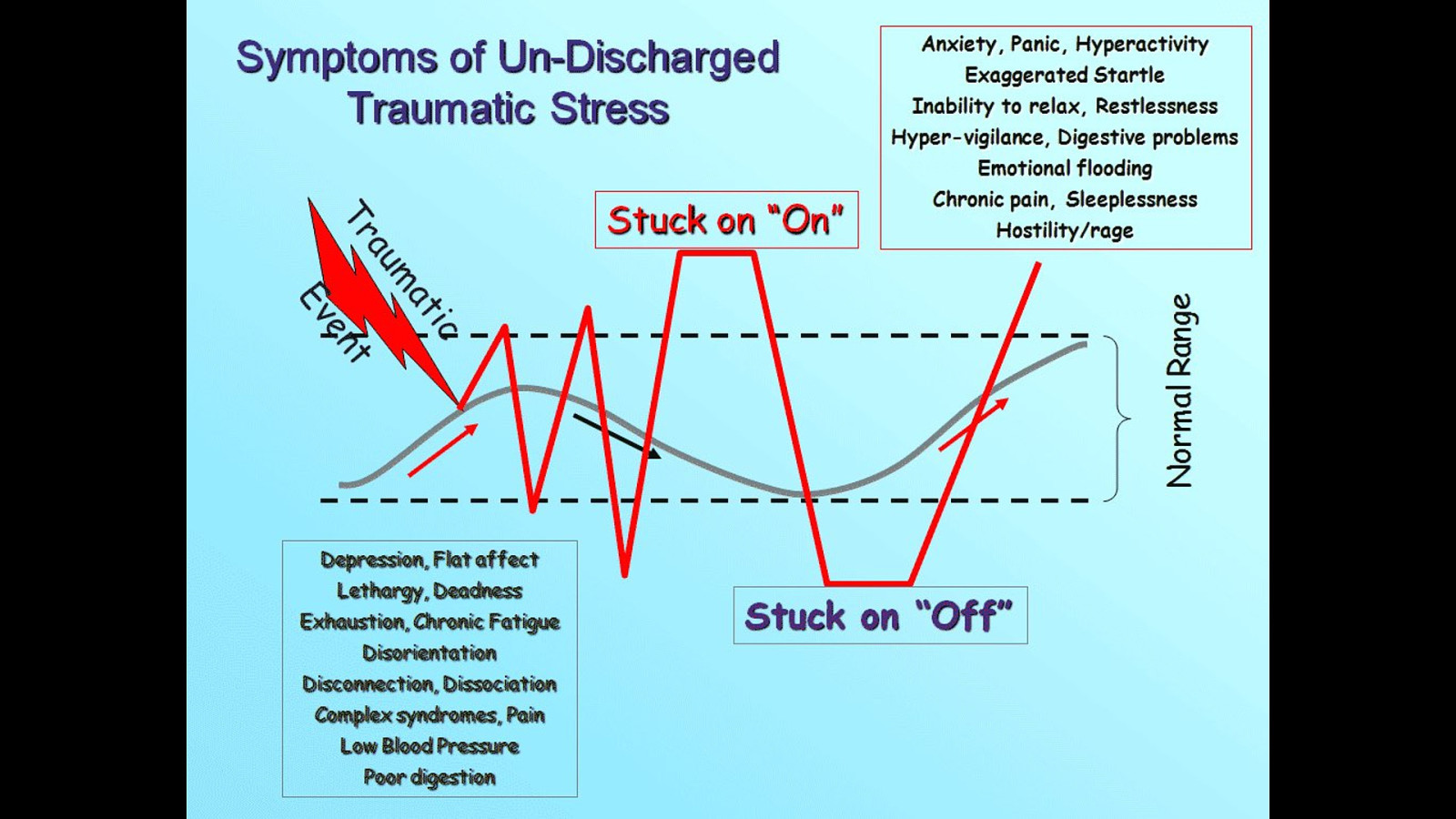
Sufferers of post-traumatic stress continue to feel these fight, flight, and freeze responses long after the trauma has passed, because our brains are unable to differentiate between the memory of trauma and an actually occurring event. When activated or triggered, the brain reverts to these behaviors, which are then expressed in the person’s body (through posture, disassociation, muscle tension, etc).
The same can occur to organizations - once an organization has experienced a trauma (a large outage, say) the “memory” of that trauma leads to a deregulated state whenever activated (by symptoms of similar indicators, such as system alerts, customer issues, and more). The organization will insist on revisiting the same fight, flight, or freeze response as the embedded trauma has caused, which, like a triggered post-traumatic stress sufferer, is a false equivalency.
One of the treatments for post-traumatic stress is Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), in which the patient’s difficult memories are offset with a positive association that is reinforced through external stimuli. The same can be done for organizations - removing the inaccurate traumatic associations of previous outages and organizational pain through game days, and other techniques, we can reduce the “scar tissue” of our organization and move forward in a balanced manner.
Video
Resources
The following resources were mentioned during the presentation or are useful additional information.